Cloud Computing: The Future of Business Operations

Cloud computing has become an essential component of modern business strategies. It has revolutionized how companies store, access, and manage data, providing unparalleled flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency. As businesses increasingly embrace digital transformation, cloud computing continues to shape the future of operations across industries.
What is Cloud Computing?
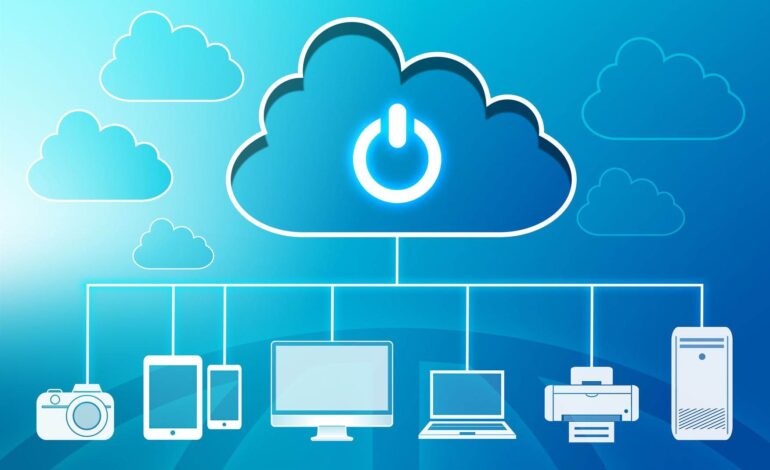
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services—such as storage, processing power, databases, and networking—over the internet. Instead of owning physical data centers or servers, businesses can rent these resources on-demand from cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
This “as-a-service” model enables companies to access powerful computing capabilities without the upfront cost of infrastructure.
Key Benefits of Cloud Computing for Businesses
1. Cost Efficiency
One of the most significant advantages of cloud computing is its cost-effectiveness. Businesses can avoid the high costs of purchasing and maintaining physical hardware, as well as the expense of hiring specialized IT staff for on-premise servers.
2. Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud services allow businesses to scale resources up or down based on demand. This flexibility ensures that companies pay only for what they use and can adapt quickly to changing market conditions.
3. Remote Work Enablement
Cloud computing has been instrumental in supporting remote work, especially during global disruptions like the COVID-19 pandemic. Employees can access data and applications from anywhere, ensuring business continuity.
4. Enhanced Collaboration
Cloud platforms facilitate seamless collaboration by enabling team members to work on shared documents and projects in real time, regardless of their physical location.
5. Disaster Recovery and Backup
With cloud-based disaster recovery solutions, businesses can store backups in secure, geographically distributed data centers. This ensures quick recovery of critical data in the event of a system failure or cyberattack.
Types of Cloud Computing Models
Public Cloud
Operated by third-party providers, public clouds are accessible over the internet. They are cost-effective and suitable for small to medium-sized businesses with limited budgets.
Private Cloud
Private clouds are dedicated to a single organization, offering greater control and customization. They are ideal for companies handling sensitive data, such as financial institutions.
Hybrid Cloud
Combining public and private clouds, hybrid models provide a balance of security and scalability. They allow businesses to keep sensitive data private while leveraging public cloud resources for less critical workloads.
Industries Leveraging Cloud Computing
1. E-commerce
Online retailers use cloud computing to manage large volumes of customer data, handle spikes in traffic, and deliver personalized shopping experiences.
2. Healthcare
Cloud technology enables secure storage of patient records, facilitates telemedicine, and supports advanced analytics for medical research.
3. Education
Educational institutions leverage cloud platforms for virtual learning environments, providing students and teachers with access to resources and tools from anywhere.
4. Finance
Banks and financial firms rely on cloud computing for fraud detection, secure transactions, and regulatory compliance.
5. Entertainment
Streaming platforms like Netflix and Spotify use the cloud to deliver content seamlessly to millions of users worldwide.
Challenges in Cloud Computing Adoption
Data Security and Privacy
While cloud providers implement robust security measures, businesses must still address concerns related to unauthorized access, data breaches, and regulatory compliance.
Downtime and Reliability
Outages at cloud providers can disrupt business operations. Companies must have contingency plans in place to mitigate potential downtime.
Vendor Lock-In
Switching between cloud providers can be challenging due to differences in infrastructure, services, and data migration processes.
Future Trends in Cloud Computing
1. Edge Computing
By processing data closer to its source, edge computing reduces latency and enhances performance, making it a critical advancement for IoT (Internet of Things) applications.
2. Multi-Cloud Strategies
Many businesses are adopting multi-cloud approaches, using services from multiple providers to reduce reliance on a single vendor and enhance operational resilience.
3. AI and Machine Learning Integration
Cloud platforms are increasingly incorporating AI and machine learning tools, enabling businesses to analyze data more efficiently and make data-driven decisions.
4. Sustainability in Cloud Computing
As concerns about environmental impact grow, cloud providers are investing in green data centers powered by renewable energy, promoting sustainability in tech.
Cloud computing has firmly established itself as the backbone of modern business operations. By enabling agility, scalability, and innovation, it empowers companies to thrive in a competitive and ever-changing landscape.